6.3 EMP_cor_analysis
In multi-omics data analysis, it is common to observe the relationships between features through a correlation coefficient matrix.
The module
EMP_cor_analysis automatically selects the intersection of data without missing values from two project datasets for analysis when calculating correlations.
6.3.1 Explore the correlation between microbial data and sample-related data
🏷️Example1:Analysis of the correlation between microbial species annotation data and scale scoring data.
Extract the assay of taxonomy, use module EMP_identify_assay to screen the core data, use module EMP_collapse to collapse out genus-level data, and use module EMP_decostand to standardize relative abundance.
micro_data <- MAE |>
EMP_assay_extract('taxonomy') |>
EMP_identify_assay(method='default') |>
EMP_collapse(estimate_group = 'Genus',collapse_by = 'row') |>
EMP_decostand(method='relative')
micro_data
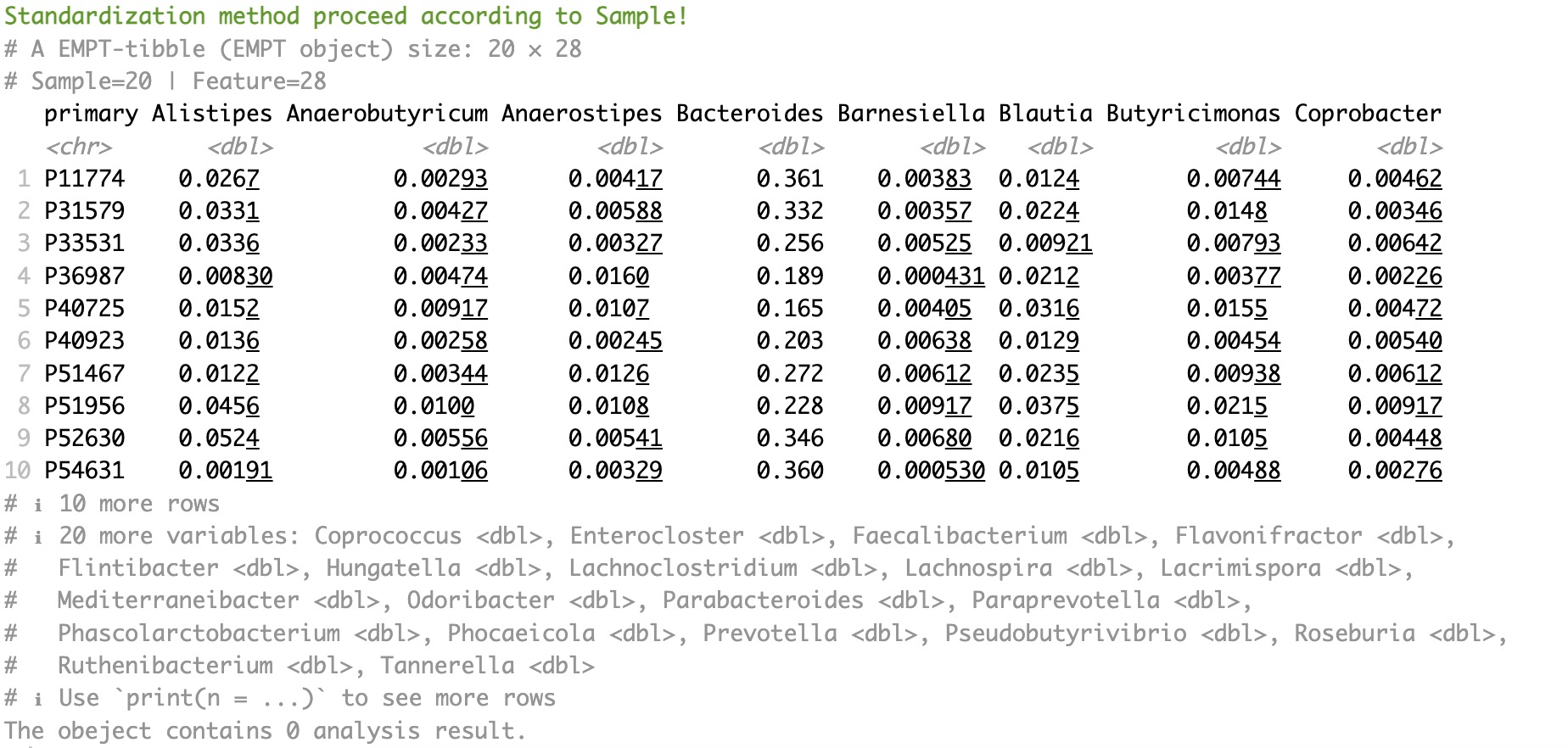
Then, extract the assay of taxonomy from the MAE object, and further extract the scale score data of the corresponding coldata.
meta_data <- MAE |>
EMP_assay_extract('taxonomy') |>
EMP_coldata_extract(action = 'add',
coldata_to_assay = c('SAS','SDS','HAMA','HAMD','PHQ9','GAD7'))
meta_data
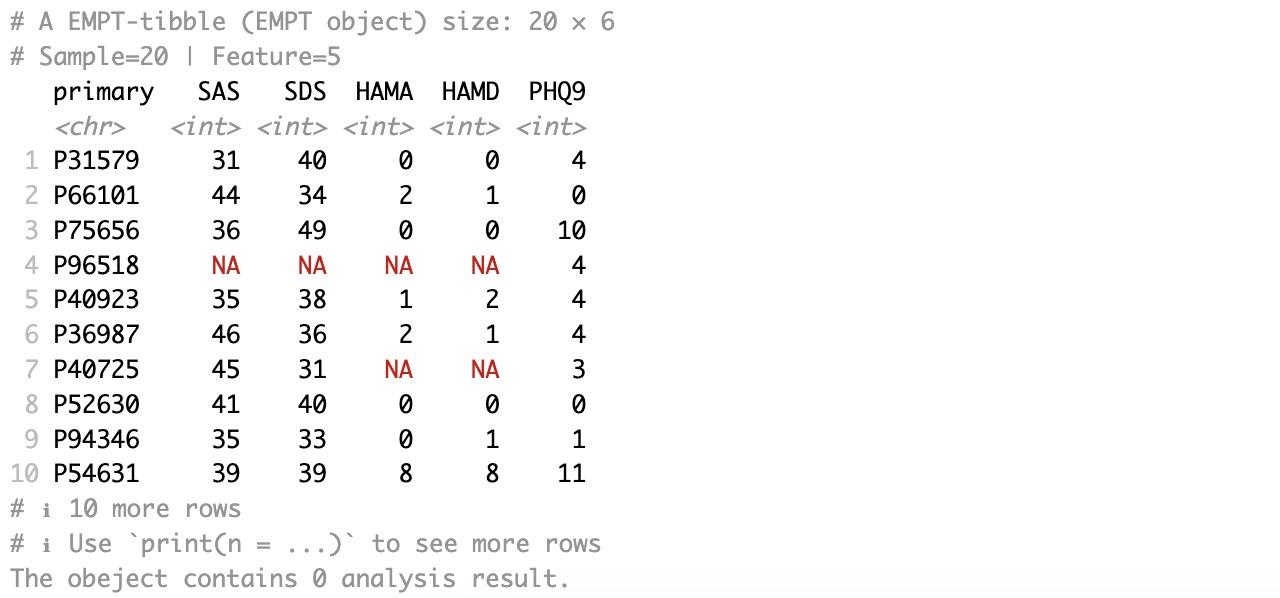
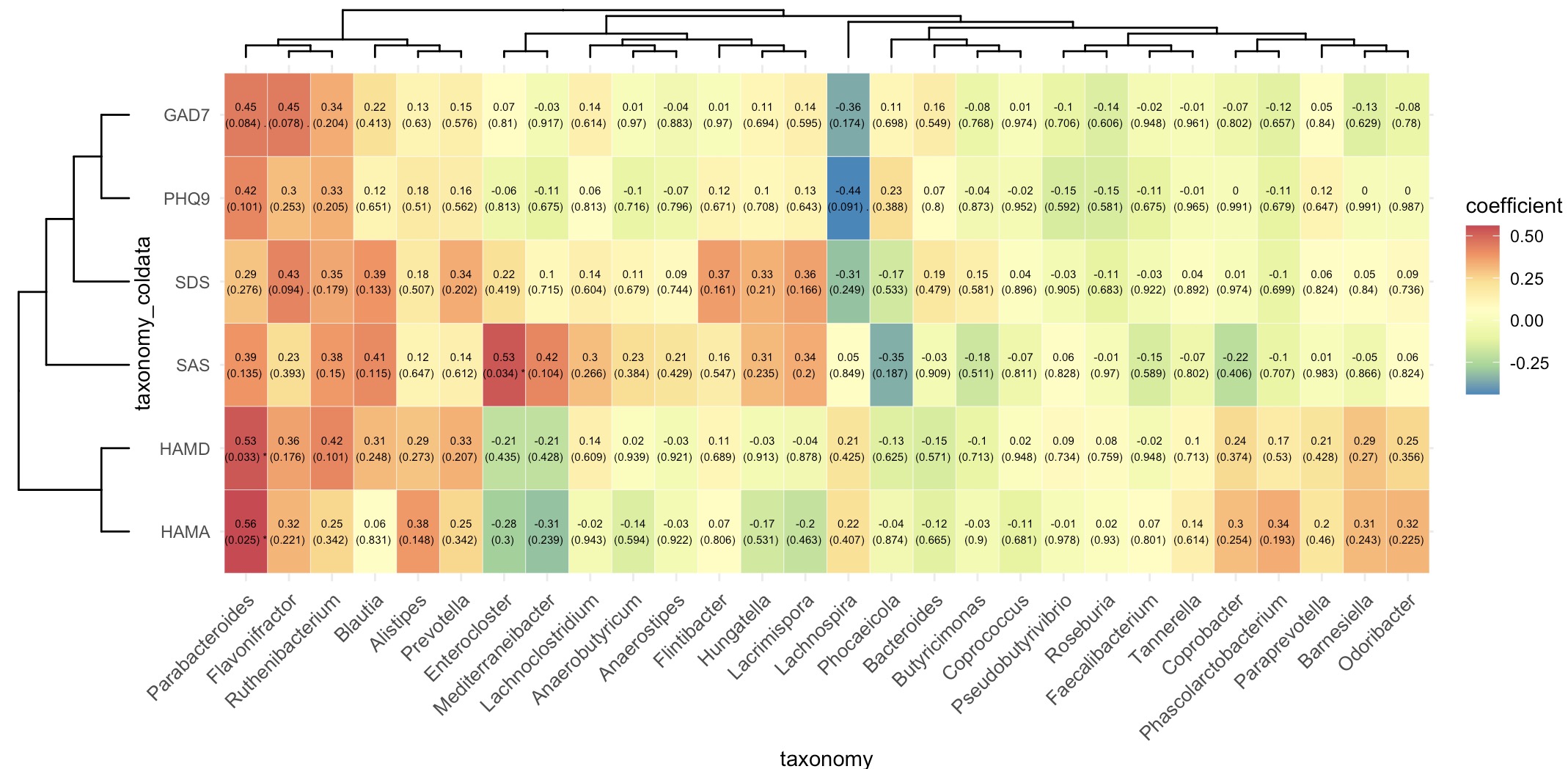
Finally, the microbial abundance data and the scale score data are combined into an EMP object using the + symbol. The correlation analysis and visualization are completed using the modules EMP_cor_analysis and EMP_heatmap_plot.
(micro_data + meta_data) |>
EMP_cor_analysis() |>
EMP_heatmap_plot(label_size=2,palette='Spectral',
clust_row=TRUE,clust_col=TRUE)
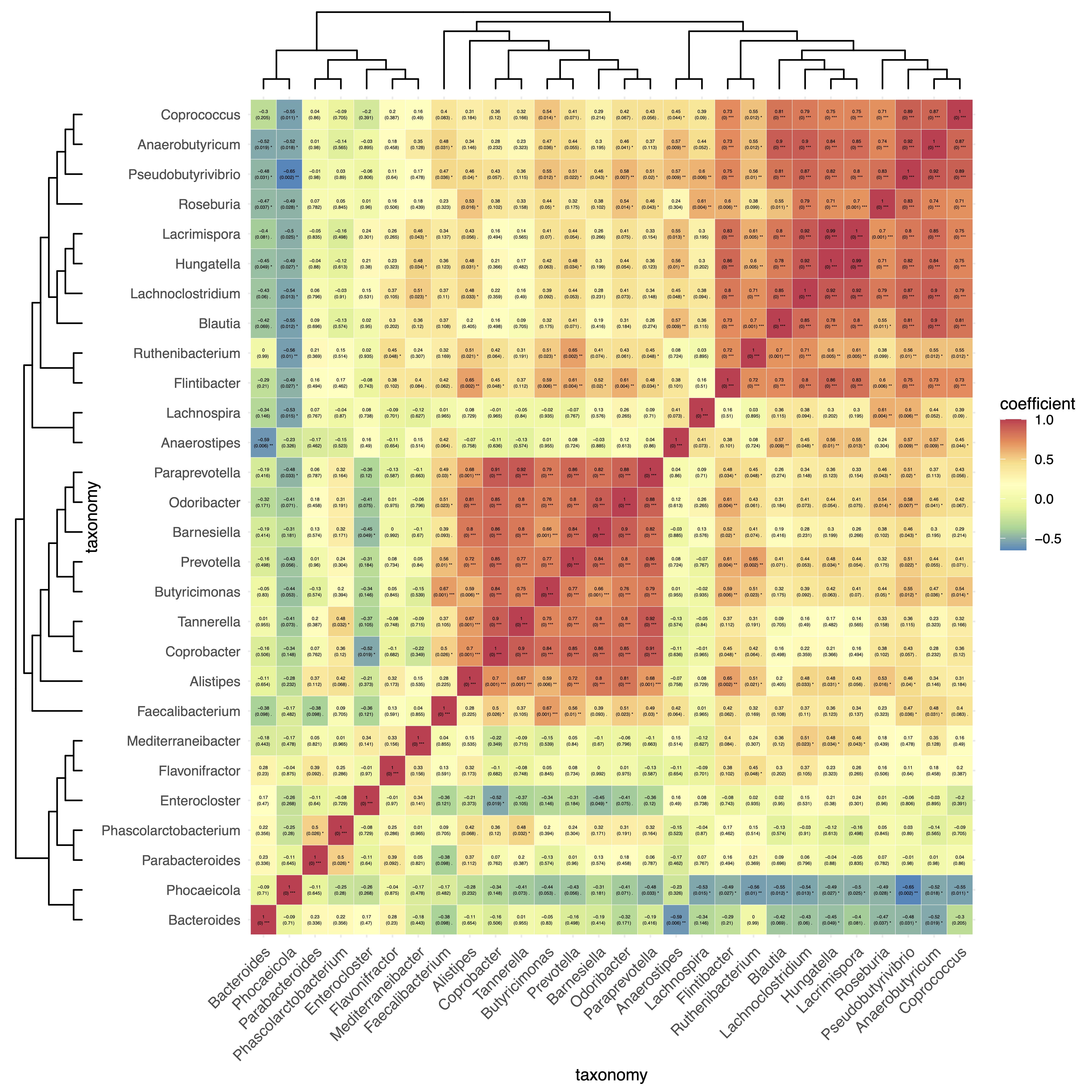
🏷️Example2: Analyse the interrelationships among microbiota.
① In this example, using
NULL here can create an EMP object with only one project.② When the
EMP object contains only one project, autocorrelation calculations will be performed.③ To draw a co-occurrence network diagram of microbial communities, users can first use the parameter
action='get' to obtain the correlation adjacency matrix, and then import it into specialized network analysis tools (such as Cytoscape, MENA, and Gephi) for further analysis.
(micro_data + NULL) |>
EMP_cor_analysis() |>
EMP_heatmap_plot(label_size=1,palette='Spectral',clust_row=TRUE,clust_col=TRUE)
6.3.2 Investigate the correlation between differential functional genes of microbiota and differential host genes expression
🏷️Example: Analysis of the correlation between differential functional genes of microbiota and differential host gene expression.
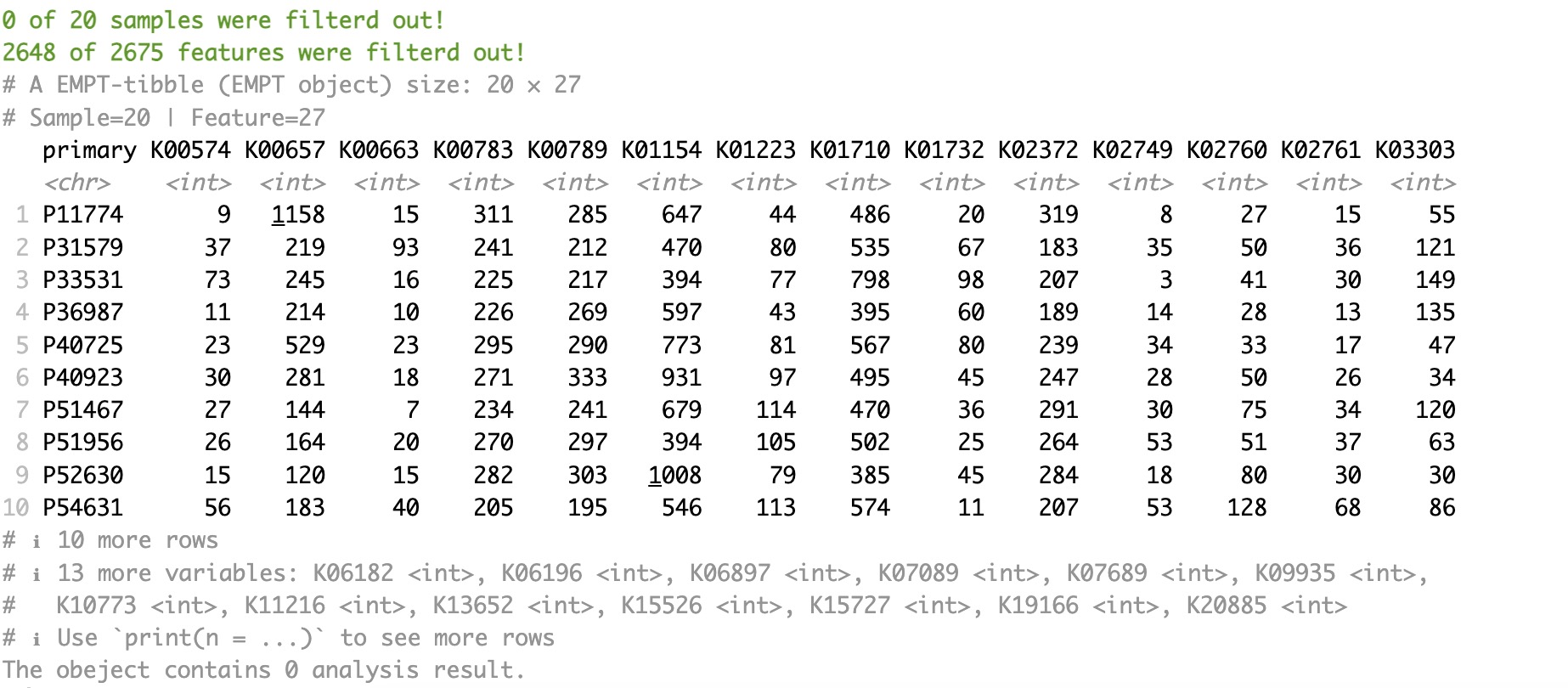
Firstly, extract the assay of geno_ko from the MAE object. Utilize module EMP_identify_assay to filter sparse genes. Apply module EMP_diff_analysis for difference analysis using DESeq2 while accounting for batch issues caused by regional factors. And select KO genes with p-values lower than 0.05.
ko_data <- MAE |>
EMP_assay_extract('geno_ko') |>
EMP_identify_assay(method='edgeR') |>
EMP_diff_analysis(method='DESeq2',.formula = ~Region+Group) |>
EMP_filter(feature_condition = pvalue < 0.05)
ko_data
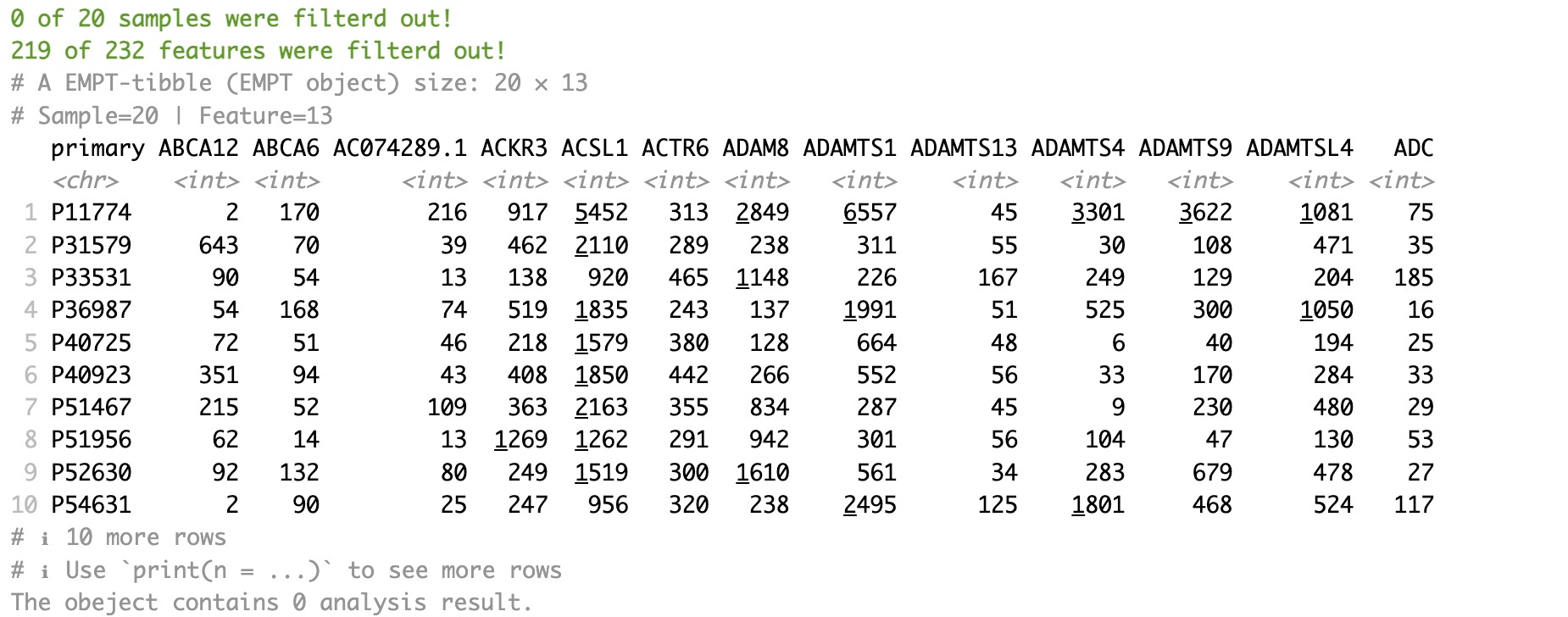
Secondly, extract the assay of host_gene from the MAE object. Utilize module EMP_identify_assay to filter sparse genes. Apply module EMP_diff_analysis for difference analysis using DESeq2 while accounting for batch issues caused by regional factors. And select genes with p-values lower than 0.05.
host_gene <- MAE |>
EMP_assay_extract('host_gene') |>
EMP_identify_assay(method='edgeR') |>
EMP_diff_analysis(method='DESeq2',.formula = ~Region+Group) |>
EMP_filter(feature_condition = pvalue < 0.05)
host_gene
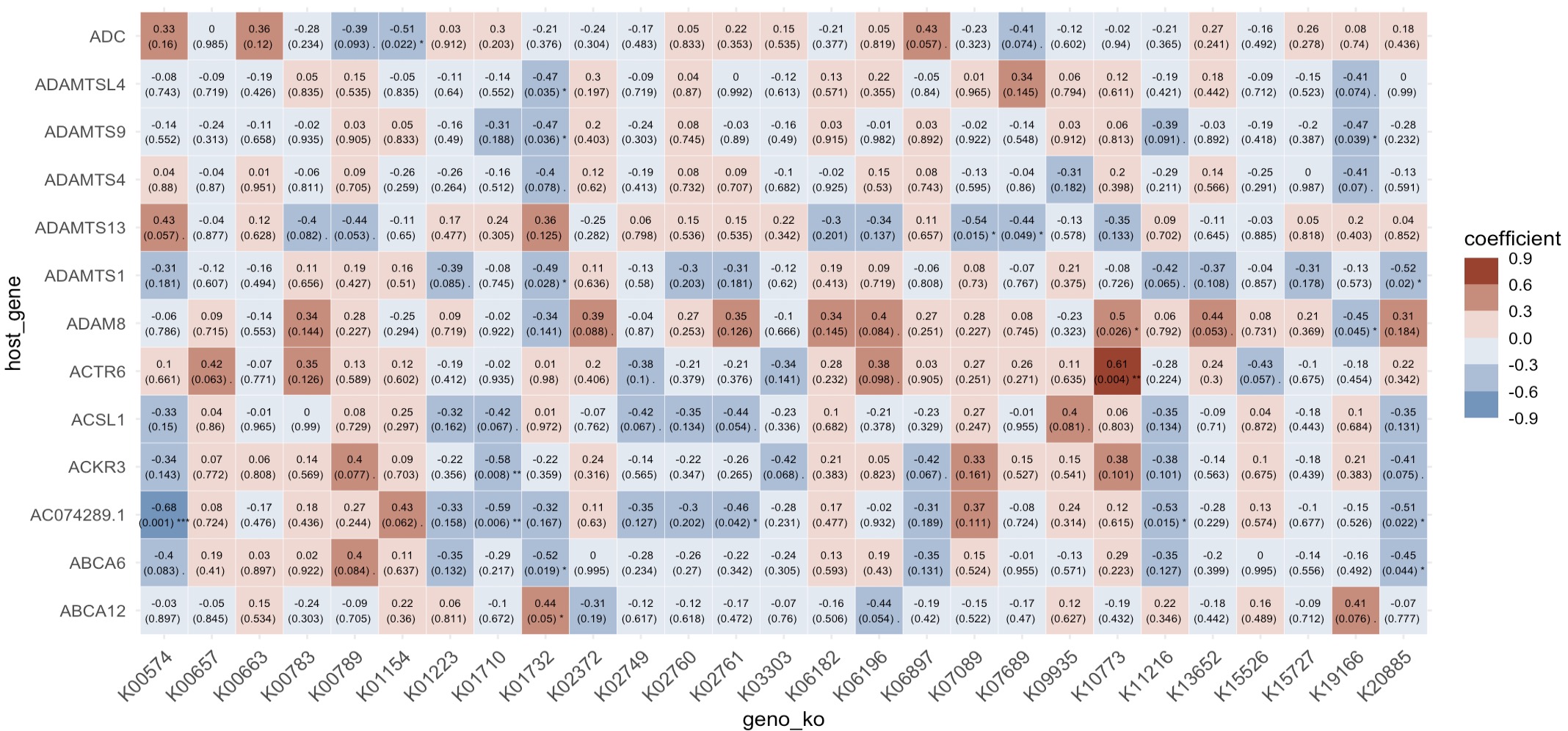
Finally, use the + symbol to merge the ko_data and host_gene into an EMP object. Modules EMP_cor_analysis and EMP_heatmap_plot are utilized to perform correlation analysis and visualization.
(ko_data + host_gene) |>
EMP_cor_analysis() |>
EMP_heatmap_plot()
6.3.3 Explore multiple correlations
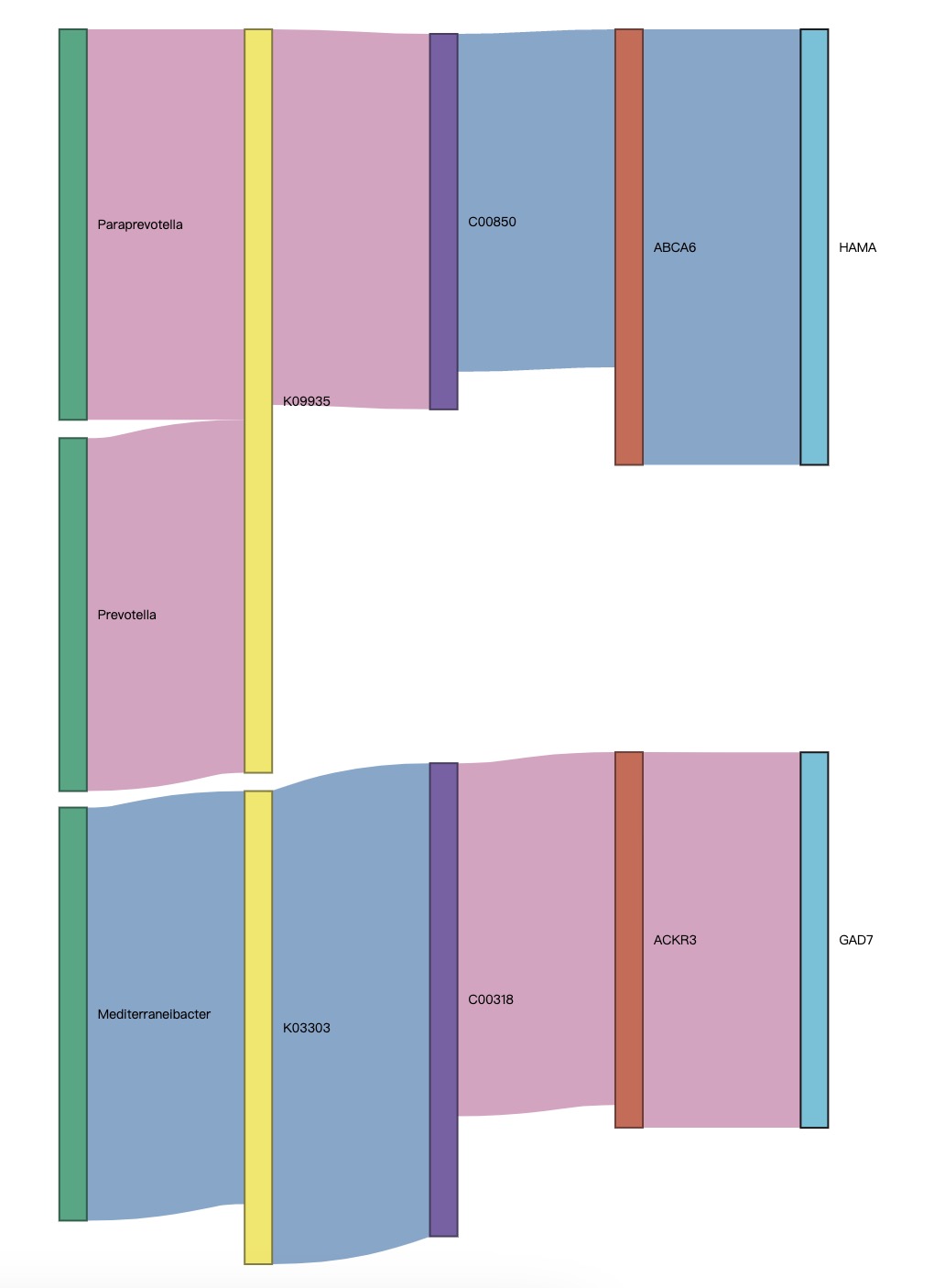
The module EMP_cor_analysis is capable of calculating the interrelationships between multi-omics project datasets. We can separately calculate the distinctive features between individual project datasets, use the + symbol to merge the projects and perform correlation tests in the order of combination. Module EMP_sankey_plot can draw a correlation Sankey diagram based on the results of multiple correlations.
① In the correlation Sankey diagram, red indicates positive correlation and blue indicates negative correlation.
② The correlation Sankey diagram evaluates the relationships between each node, and isolated nodes will be filtered out.
③ The parameters
pvalue and rvalue can adjust the number of edges.
🏷️Example: Explore the multiple correlations between microbial, functional gene, metabolite, host gene, and sample-related data.
micro_data <- MAE |>
EMP_assay_extract('taxonomy') |>
EMP_identify_assay(method='default') |>
EMP_collapse(estimate_group = 'Genus',collapse_by = 'row') |>
EMP_decostand(method='relative')
ko_data <- MAE |>
EMP_assay_extract('geno_ko') |>
EMP_identify_assay(method='edgeR') |>
EMP_diff_analysis(method='DESeq2',.formula = ~Region+Group) |>
EMP_filter(feature_condition = pvalue < 0.05)
metabolite_data <- MAE |>
EMP_assay_extract(experiment = 'untarget_metabol') |>
EMP_collapse(estimate_group = 'MS2kegg',collapse_by='row',
na_string = c("NA", "null", "","-"),
method = 'mean',collapse_sep = '+') |>
EMP_decostand(method = 'relative') |>
EMP_dimension_analysis(method = 'pls',estimate_group = 'Group') |>
EMP_filter(feature_condition = VIP >2)
host_gene <- MAE |>
EMP_assay_extract('host_gene') |>
EMP_identify_assay(method='edgeR') |>
EMP_diff_analysis(method='DESeq2',.formula = ~Region+Group) |>
EMP_filter(feature_condition = pvalue < 0.05)
meta_data<- MAE |>
EMP_assay_extract('taxonomy') |>
EMP_coldata_extract(action = 'add',
coldata_to_assay = c('SAS','SDS','HAMA','HAMD','PHQ9','GAD7'))
(micro_data + ko_data + metabolite_data + host_gene + meta_data) |>
EMP_cor_analysis() |>
EMP_sankey_plot()
